A fast reverse proxy to help you expose local server behind a NAT or firewall to the internet
Based on frp@github, I wrote this lab to show how to use this tool.
[Topology]
H1(private server, running frp client)…………..r1 (router + NAT) --------------r2 ------------h3 (public node)
|
h2 (public server, running frp server)
Before you run this example in mininet, you have to install go language in your environment.
You also need to download frp from github and compile the frps and frpc.
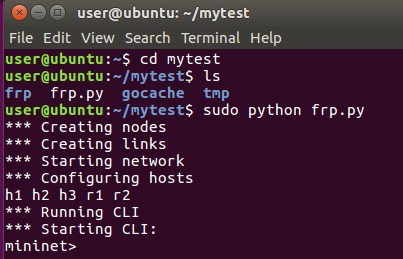
[mininet-script]
|
#!/usr/bin/python from mininet.net import Mininet from mininet.link import Link, TCLink from mininet.cli
import CLI from mininet.log import setLogLevel def topology(): "Create a
network." net = Mininet() print "*** Creating
nodes" h1 = net.addHost( 'h1', ip="192.168.1.1/24")
#private server h2 = net.addHost( 'h2', ip="1.1.1.1/24")
#public server h3 = net.addHost( 'h3', ip="2.2.2.2/24")
#public node r1 = net.addHost( 'r1') r2 = net.addHost( 'r2')
#### h1 --- r1 ---r2----h3 ####
| ####
h2 print "*** Creating
links" net.addLink(h1, r1) net.addLink(r1, r2) net.addLink(r2, h2) net.addLink(r2, h3) print "*** Starting
network" net.build() print "*** Running
CLI" r1.cmd("echo
1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward") r2.cmd("echo
1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward") r1.cmd("ifconfig
r1-eth0 0") r1.cmd("ifconfig
r1-eth1 0") r2.cmd("ifconfig
r2-eth0 0") r2.cmd("ifconfig
r2-eth1 0") r2.cmd("ifconfig
r2-eth2 0") r1.cmd("ip addr add 192.168.1.254/24 brd + dev r1-eth0") r1.cmd("ip addr add 12.1.1.1/24 brd + dev r1-eth1") r2.cmd("ip addr add 12.1.1.2/24 brd + dev r2-eth0") r2.cmd("ip addr add 1.1.1.254/24 brd + dev r2-eth1") r2.cmd("ip addr add 2.2.2.254/24 brd + dev r2-eth2") h1.cmd("ip route add default via 192.168.1.254") h2.cmd("ip route add default via 1.1.1.254") h3.cmd("ip route add default via 2.2.2.254") r2.cmd("ip route add 12.1.1.0/24 via 12.1.1.1") r1.cmd("ip route add 1.1.1.0/24 via 12.1.1.2") r1.cmd("ip route add 2.2.2.0/24 via 12.1.1.2") r1.cmd("iptables
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -o r1-eth1
-j MASQUERADE") CLI( net
) print "*** Stopping
network" net.stop() if __name__ == '__main__': setLogLevel( 'info' ) topology() |
[execution]
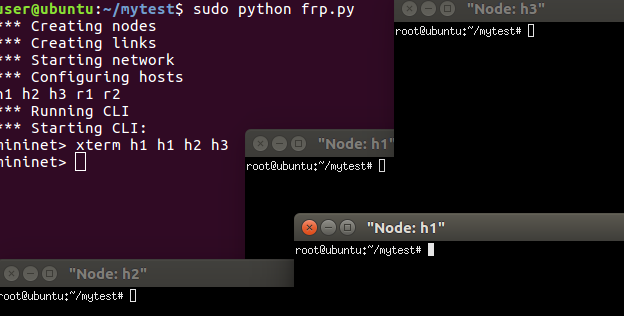
Open two terminal for h1, one terminal for h2, and one terminal for h3
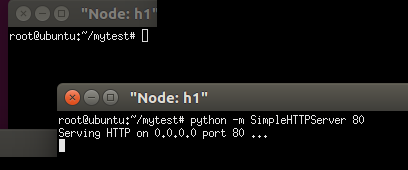
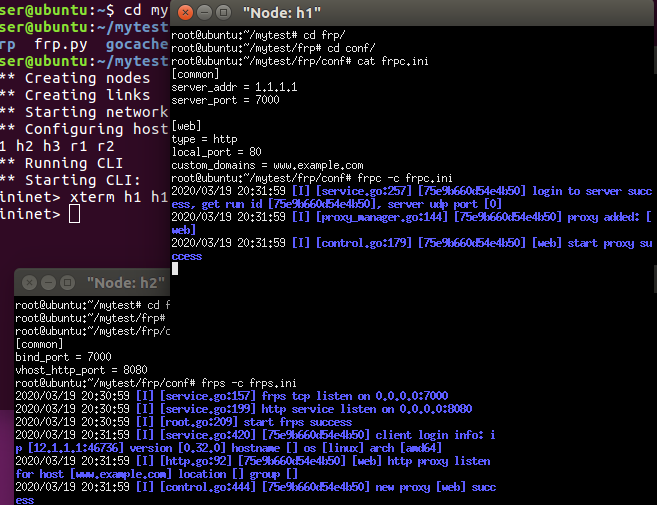
At h1 terminal, run the web service
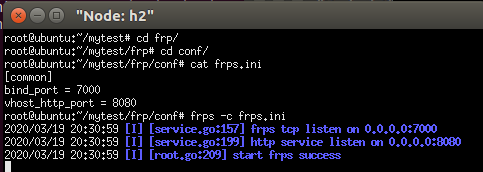
At h2 terminal, do the frps configuration and then run the frps.
At h1 terminal, do the frpc configuration and then run the frpc.
At h3 terminal, edit /etc/hosts file to make www.example.com map to the ip address of h2 (1.1.1.1). Then you can use curl to test the connectivity with h1.
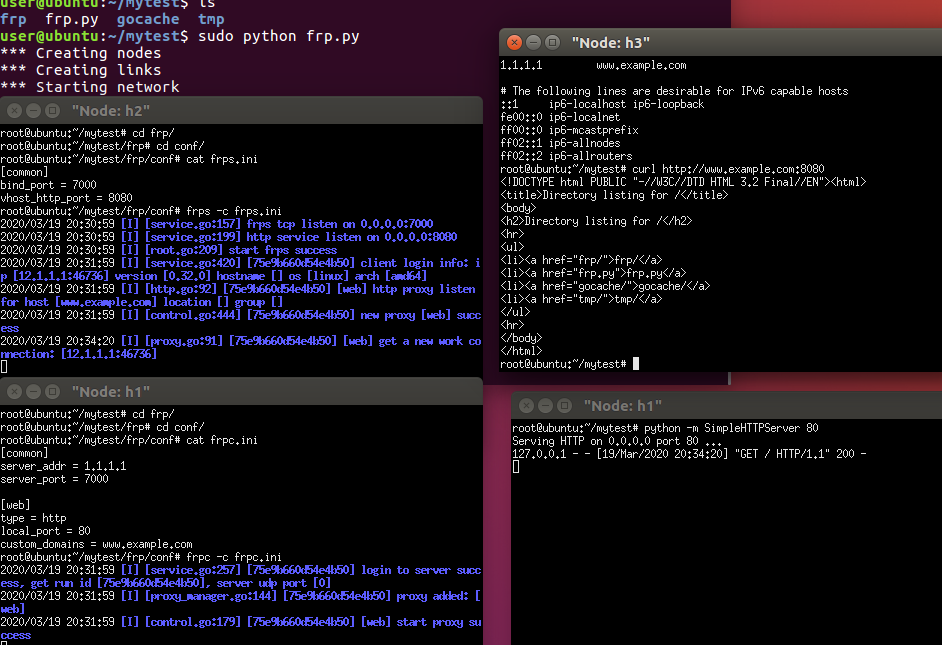
H3 can access the web server in H1.
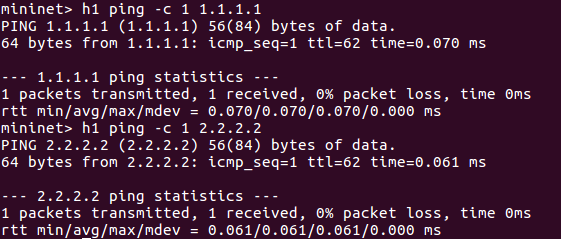
Ping test.
H1 (private node) can ping public host (h2 and h3)
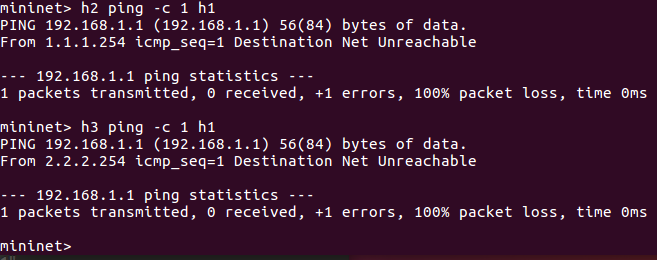
But public node (h2 and h3) cannot ping h1.
Dr. Chih-Heng Ke (smallko@gmail.com)
Department
of Computer Science and Information Engineering,
National
Quemoy University, Kinmen,
Taiwan.