Find the maximum capacity path with Dijkstra’s Algorithm in accordance with current network status
[Topology]
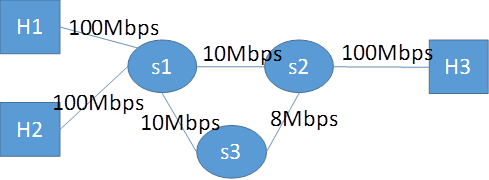
H2 will send traffic to H3 and H1 will also send traffic to H3. If we use dijkstra’s algorithm to find the shortest path. These two flows will go via s1 and s2 and they will compete for bandwidth.
So we will let the H2 send the traffic to H3 first. This flow will go via s1 and s2 and then reach H3. Following, we will let the flow sent from H1 to H3 use the modified version of Dijkstra’s Algorithm to find the maximum capacity path. Therefore, this flow will go via s1,s3,s2, and then H3.
[mininet-script]
|
from mininet.net import Mininet from mininet.node
import Controller, RemoteController, OVSKernelSwitch, UserSwitch, OVSSwitch from mininet.cli
import CLI from mininet.log import setLogLevel from mininet.link
import Link, TCLink def topology():
net = Mininet( controller=RemoteController, link=TCLink,
switch=OVSSwitch ) #
Add hosts and switches
h1= net.addHost( 'h1',
mac="00:00:00:00:00:01" ) h2
= net.addHost( 'h2',
mac="00:00:00:00:00:02" ) h3
= net.addHost( 'h3',
mac="00:00:00:00:00:03" ) s1
= net.addSwitch( 's1' ) s2
= net.addSwitch( 's2' ) s3
= net.addSwitch( 's3' ) c0
= net.addController( 'c0', controller=RemoteController, ip='127.0.0.1',
port=6633 )
linkopt1=dict(bw=10,delay='1ms',loss=0)
linkopt2=dict(bw=8,delay='1ms',loss=0)
linkopt3=dict(bw=100,delay='1ms',loss=0) net.addLink( h1, s1, **linkopt3) net.addLink( h2, s1, **linkopt3) net.addLink( h3, s2, **linkopt3) net.addLink( s1, s2, **linkopt1) net.addLink( s1, s3, **linkopt1) net.addLink( s2, s3, **linkopt2) net.build()
c0.start()
s1.start( [c0] )
s2.start( [c0] )
s3.start( [c0] )
print "*** Running CLI"
CLI( net )
print "*** Stopping network" net.stop() if __name__ == '__main__': setLogLevel(
'info' ) topology() |
Please prepare one text file (bw.txt) and put it under ryu/ryu/app folder. This text file will tell the controller application the link bandwidth between switches. Because we are running experiments under mininet. We cannot simply send feature requests to switches and get the correct port settings. (In the mininet, TC is used to limit the bandwidth). The first column is the first switch ID, the second is the second switch ID, and the third is bandwidth in Mbps. (1 2 10 means the link between s1 and s2 is 1OMbps)
|
1 2 10 1 3 10 2 3 8 |
[ryu application]
|
# Copyright (C) 2011 Nippon Telegraph and
Telephone Corporation. # # Licensed under the Apache License,
Version 2.0 (the "License"); # you may not
use this file except in compliance with the License. # You may obtain a copy of the License at # #
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 # # Unless required by applicable law or
agreed to in writing, software # distributed under the License is
distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
KIND, either express or # implied. # See the License for the specific
language governing permissions and # limitations
under the License. from ryu.base
import app_manager from ryu.controller
import mac_to_port from ryu.controller
import ofp_event from ryu.controller.handler
import CONFIG_DISPATCHER, MAIN_DISPATCHER, DEAD_DISPATCHER from ryu.controller.handler
import set_ev_cls from ryu.ofproto
import ofproto_v1_3 from ryu.lib.mac import haddr_to_bin from ryu.lib.packet
import packet from ryu.lib.packet
import ethernet from ryu.lib.packet
import ether_types from ryu.lib import mac from ryu.topology
import event, switches from ryu.topology.api
import get_switch, get_link from ryu.app.wsgi
import ControllerBase from collections import defaultdict from ryu.lib import hub from operator import attrgetter from datetime
import datetime import time #switches myswitches = [] #mymac[srcmac]->(switch, port) mymac={} #adjacency map [sw1][sw2]->port from
sw1 to sw2 adjacency=defaultdict(lambda:defaultdict(lambda:None)) datapath_list={} byte=defaultdict(lambda:defaultdict(lambda:None)) clock=defaultdict(lambda:defaultdict(lambda:None)) bw_used=defaultdict(lambda:defaultdict(lambda:None)) bw_available=defaultdict(lambda:defaultdict(lambda:None)) bw=defaultdict(lambda:defaultdict(lambda:None)) target_srcmac="00:00:00:00:00:01" target_dstmac="00:00:00:00:00:03" def max_abw(abw,
Q):
max = float('-Inf')
node = 0
for v in Q: if abw[v]
> max: max = abw[v] node = v
return node def get_path2 (src,dst,first_port,final_port):
global bw_available
print "Dijkstra's widest path
algorithm"
print "src=",src,"
dst=",dst, " first_port=", first_port,
" final_port=", final_port
#available bandwidth
abw = {}
previous = {}
for dpid in myswitches: abw[dpid] = float('-Inf') previous[dpid] = None
abw[src]=float('Inf')
Q=set(myswitches)
print "Q:", Q
#print time.time()
while len(Q)>0: u = max_abw(abw, Q) Q.remove(u) print "Q:", Q,
"u:", u for p in myswitches: if
adjacency[u][p]!=None: link_abw = bw_available[str(u)][str(p)]
print "link_abw:", str(u),"->",str(p),":",link_abw, "kbps"
#alt=max(abw[p], min(width[u], abw_between(u,p))) if abw[u] < link_abw:
tmp = abw[u]
else:
tmp = link_abw if
abw[p] > tmp:
alt = abw[p]
else:
alt = tmp if
alt > abw[p]:
abw[p] = alt
previous[p] = u
#print "distance=", distance, " previous=",
previous
r=[]
p=dst
r.append(p)
q=previous[p]
while q is not None: if q == src: r.append(q) break p=q r.append(p) q=previous[p]
r.reverse()
if src==dst: path=[src]
else: path=r
# Now add the ports
r = []
in_port = first_port
for s1,s2 in zip(path[:-1],path[1:]): out_port
= adjacency[s1][s2] r.append((s1,in_port,out_port)) in_port
= adjacency[s2][s1]
r.append((dst,in_port,final_port))
return r def minimum_distance(distance, Q):
#print "minimum_distance() is
called", " distance=", distance, " Q=", Q
min = float('Inf')
node = 0
for v in Q: if distance[v] < min: min =
distance[v] node = v
return node def get_path (src,dst,first_port,final_port):
#Dijkstra's algorithm
global myswitches, adjacency
print "Dijkstra's shortest path
algorithm"
print "get_path is called, src=",src," dst=",dst, " first_port=", first_port,
" final_port=", final_port
distance = {}
previous = {}
for dpid in myswitches: distance[dpid] = float('Inf') previous[dpid] = None
distance[src]=0
Q=set(myswitches)
#print "Q=", Q
while len(Q)>0: u = minimum_distance(distance,
Q) #print "u=", u Q.remove(u) #print "After
removing ", u, " Q=", Q for p in myswitches: if
adjacency[u][p]!=None:
#print u, "--------",
p w
= 1 if
distance[u] + w < distance[p]:
distance[p] = distance[u] + w
previous[p] = u
#print "distance=", distance, " previous=",
previous
r=[]
p=dst
r.append(p)
q=previous[p]
while q is not None: if q == src: r.append(q) break p=q r.append(p) q=previous[p]
r.reverse()
if src==dst: path=[src]
else: path=r
# Now add the ports
r = []
in_port = first_port
for s1,s2 in zip(path[:-1],path[1:]): out_port
= adjacency[s1][s2] r.append((s1,in_port,out_port)) in_port
= adjacency[s2][s1]
r.append((dst,in_port,final_port))
return r class ProjectController(app_manager.RyuApp): OFP_VERSIONS =
[ofproto_v1_3.OFP_VERSION] def
__init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(ProjectController, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.mac_to_port = {} self.topology_api_app = self self.datapaths = {} self.monitor_thread = hub.spawn(self._monitor)
global bw
try:
fin = open("bw.txt", "r")
for line in fin:
a=line.split()
if a: bw[str(a[0])][str(a[1])]=int(a[2])
bw[str(a[1])][str(a[0])]=int(a[2])
fin.close()
except IOError:
print "make bw.txt ready" #print
"bw:", bw @set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPStateChange,
[MAIN_DISPATCHER, DEAD_DISPATCHER]) def
_state_change_handler(self, ev): datapath = ev.datapath if
ev.state == MAIN_DISPATCHER:
if not datapath.id in self.datapaths:
#self.logger.debug('register datapath: %016x', datapath.id)
print 'register datapath:', datapath.id
self.datapaths[datapath.id] = datapath elif ev.state ==
DEAD_DISPATCHER:
if datapath.id in self.datapaths:
#self.logger.debug('unregister datapath:
%016x', datapath.id)
print 'unregister datapath:', datapath.id
del self.datapaths[datapath.id] def
_monitor(self):
while True:
for dp in self.datapaths.values():
self._request_stats(dp)
hub.sleep(3) def
_request_stats(self, datapath): #self.logger.debug('send stats request: %016x',
datapath.id)
#print 'send stats request:', datapath.id ofproto = datapath.ofproto
parser = datapath.ofproto_parser req = parser.OFPFlowStatsRequest(datapath) datapath.send_msg(req) req = parser.OFPPortStatsRequest(datapath, 0, ofproto.OFPP_ANY) datapath.send_msg(req) @set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPFlowStatsReply, MAIN_DISPATCHER) def
_flow_stats_reply_handler(self, ev):
body = ev.msg.body
#self.logger.info('datapath
'
#
'in-port eth-dst '
#
'out-port packets bytes')
#self.logger.info('---------------- '
#
'-------- ----------------- '
#
'-------- -------- --------')
#for stat in sorted([flow for flow in body if flow.priority
== 1],
#
key=lambda flow: (flow.match['in_port'],
#
flow.match['eth_dst'])):
#
self.logger.info('%016x %8x %17s %8x %8d %8d',
#
ev.msg.datapath.id,
#
stat.match['in_port'],
stat.match['eth_dst'],
#
stat.instructions[0].actions[0].port,
#
stat.packet_count, stat.byte_count) @set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPPortStatsReply, MAIN_DISPATCHER) def
_port_stats_reply_handler(self, ev):
global byte, clock, bw_used, bw_available
#print time.time()," _port_stats_reply_handler"
body = ev.msg.body
dpid = ev.msg.datapath.id
for stat in sorted(body, key=attrgetter('port_no')):
#print dpid, stat.port_no,
stat.tx_packets
for p in myswitches:
if adjacency[dpid][p]==stat.port_no:
#print dpid, p, stat.port_no
if byte[dpid][p]>0:
bw_used[dpid][p] =
(stat.tx_bytes - byte[dpid][p])
* 8.0 / (time.time()-clock[dpid][p])
/ 1000
bw_available[str(dpid)][str(p)]=int(bw[str(dpid)][str(p)]) * 1024.0 - bw_used[dpid][p]
print str(dpid),"->",str(p),":",bw_available[str(dpid)][str(p)],"
kbps"
#print str(dpid),"->",str(p),":", bw[str(dpid)][str(p)],"
kbps"
byte[dpid][p]=stat.tx_bytes
clock[dpid][p]=time.time()
print
"-------------------------------------------------------------------"
#self.logger.info('datapath
port '
#
'rx-pkts rx-bytes rx-error '
#
'tx-pkts tx-bytes tx-error')
#self.logger.info('---------------- -------- '
#
'-------- -------- -------- '
#
'-------- -------- --------')
#for stat in sorted(body, key=attrgetter('port_no')):
#
self.logger.info('%016x %8x %8d %8d %8d %8d %8d %8d',
#
ev.msg.datapath.id, stat.port_no,
#
stat.rx_packets, stat.rx_bytes,
stat.rx_errors,
#
stat.tx_packets, stat.tx_bytes,
stat.tx_errors) # Handy function that
lists all attributes in the given object def
ls(self,obj): print("\n".join([x for
x in dir(obj) if x[0] !=
"_"])) def
add_flow(self, datapath, in_port, dst, actions): ofproto = datapath.ofproto parser = datapath.ofproto_parser
match = datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPMatch(
in_port=in_port, eth_dst=dst) inst = [parser.OFPInstructionActions(ofproto.OFPIT_APPLY_ACTIONS, actions)]
mod = datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPFlowMod(
datapath=datapath,
match=match, cookie=0,
command=ofproto.OFPFC_ADD, idle_timeout=0, hard_timeout=0,
priority=ofproto.OFP_DEFAULT_PRIORITY,
instructions=inst) datapath.send_msg(mod) def
install_path(self, p, ev,
src_mac, dst_mac): print
"install_path is called" #print
"p=", p, " src_mac=", src_mac, " dst_mac=",
dst_mac msg = ev.msg datapath = msg.datapath ofproto = datapath.ofproto parser =
datapath.ofproto_parser for sw, in_port, out_port in p:
print src_mac,"->", dst_mac, "via ", sw,
" in_port=", in_port,
" out_port=", out_port
match=parser.OFPMatch(in_port=in_port, eth_src=src_mac, eth_dst=dst_mac)
actions=[parser.OFPActionOutput(out_port)]
datapath=datapath_list[sw]
inst = [parser.OFPInstructionActions(ofproto.OFPIT_APPLY_ACTIONS , actions)]
mod = datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPFlowMod(
datapath=datapath,
match=match, idle_timeout=0, hard_timeout=0,
priority=1, instructions=inst)
datapath.send_msg(mod) @set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPSwitchFeatures , CONFIG_DISPATCHER) def
switch_features_handler(self , ev):
print "switch_features_handler is
called"
datapath = ev.msg.datapath
ofproto = datapath.ofproto
parser = datapath.ofproto_parser
match = parser.OFPMatch()
actions = [parser.OFPActionOutput(ofproto.OFPP_CONTROLLER, ofproto.OFPCML_NO_BUFFER)]
inst = [parser.OFPInstructionActions(ofproto.OFPIT_APPLY_ACTIONS , actions)]
mod = datapath.ofproto_parser.OFPFlowMod(
datapath=datapath,
match=match, cookie=0,
command=ofproto.OFPFC_ADD, idle_timeout=0, hard_timeout=0,
priority=0, instructions=inst)
datapath.send_msg(mod) @set_ev_cls(ofp_event.EventOFPPacketIn, MAIN_DISPATCHER) def
_packet_in_handler(self, ev): global
target_srcmac, target_dstmac
#print "packet_in event:",
ev.msg.datapath.id, " in_port:", ev.msg.match['in_port'] msg = ev.msg datapath = msg.datapath ofproto = datapath.ofproto
parser = datapath.ofproto_parser in_port = msg.match['in_port'] pkt = packet.Packet(msg.data)
eth = pkt.get_protocol(ethernet.ethernet)
#print "eth.ethertype=", eth.ethertype #avodi broadcast from LLDP if
eth.ethertype==35020:
return dst = eth.dst src = eth.src dpid = datapath.id
#print "src=", src,
" dst=", dst,
" type=", hex(eth.ethertype)
#print "adjacency=", adjacency self.mac_to_port.setdefault(dpid,
{}) if
src not in mymac.keys():
mymac[src]=( dpid, in_port)
#print "mymac=", mymac if
dst in mymac.keys():
if (src==target_srcmac
and dst==target_dstmac)
or (dst==target_srcmac
and src==target_dstmac):
p = get_path2(mymac[src][0],
mymac[dst][0], mymac[src][1], mymac[dst][1]) else:
p = get_path(mymac[src][0], mymac[dst][0], mymac[src][1], mymac[dst][1])
print "Path=", p
self.install_path(p, ev,
src, dst)
out_port = p[0][2]
else:
out_port = ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD
actions = [parser.OFPActionOutput(out_port)] #
install a flow to avoid packet_in next time if
out_port != ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD:
match = parser.OFPMatch(in_port=in_port, eth_src=src, eth_dst=dst)
data=None if
msg.buffer_id==ofproto.OFP_NO_BUFFER:
data=msg.data if
out_port == ofproto.OFPP_FLOOD:
#print "FLOOD"
while len(actions) > 0 : actions.pop()
for i in range(1,23):
actions.append(parser.OFPActionOutput(i))
#print "actions=", actions
out = parser.OFPPacketOut(datapath=datapath, buffer_id=msg.buffer_id,
in_port=in_port,
actions=actions, data=data)
datapath.send_msg(out)
else:
#print "unicast"
out = parser.OFPPacketOut(
datapath=datapath,
buffer_id=msg.buffer_id, in_port=in_port,
actions=actions, data=data)
datapath.send_msg(out) events = [event.EventSwitchEnter,
event.EventSwitchLeave, event.EventPortAdd,
event.EventPortDelete, event.EventPortModify, event.EventLinkAdd, event.EventLinkDelete] @set_ev_cls(events) def
get_topology_data(self, ev):
print "get_topology_data() is
called"
global myswitches, adjacency, datapath_list switch_list = get_switch(self.topology_api_app, None) myswitches=[switch.dp.id for switch in switch_list]
for switch in switch_list:
datapath_list[switch.dp.id]=switch.dp
#print "datapath_list=", datapath_list
print "myswitches=", myswitches links_list = get_link(self.topology_api_app, None)
#print "links_list=", links_list
mylinks=[(link.src.dpid,link.dst.dpid,link.src.port_no,link.dst.port_no)
for link in links_list]
for s1,s2,port1,port2 in mylinks:
#print "type(s1)=", type(s1), " type(port1)=",
type(port1)
adjacency[s1][s2]=port1
adjacency[s2][s1]=port2 print s1,":", port1, "<--->",s2,":",port2 |
[Execution]
Open a terminal to run ryu application
Open another terminal to run the mininet script
Use xterm to open h1 h2 h3 h3
Send the traffic from h2 first.
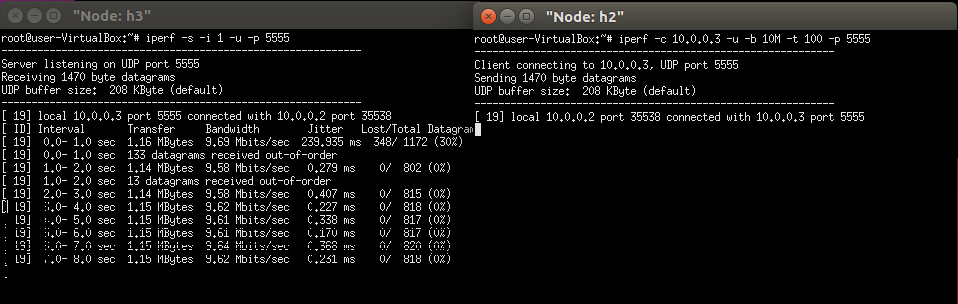
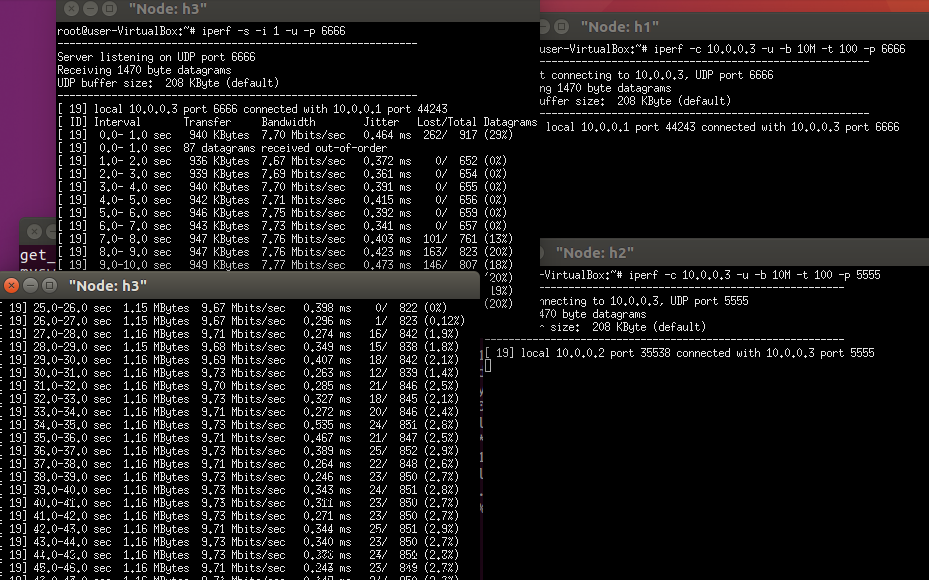
Then send the traffic from H1. From the following we can see that the flow from H2 will not be affected by the flow of H1-H3. Because the flow of H1-H3 go different path (s1,s3,and then s2).
Dr. Chih-Heng Ke
Department of Computer Science and
Information Engineering, National Quemoy University, Kinmen, Taiwan
Email: smallko@gmail.com