Tap Bridge Model: UseBridge Mode (more complicated scenario) in NS3
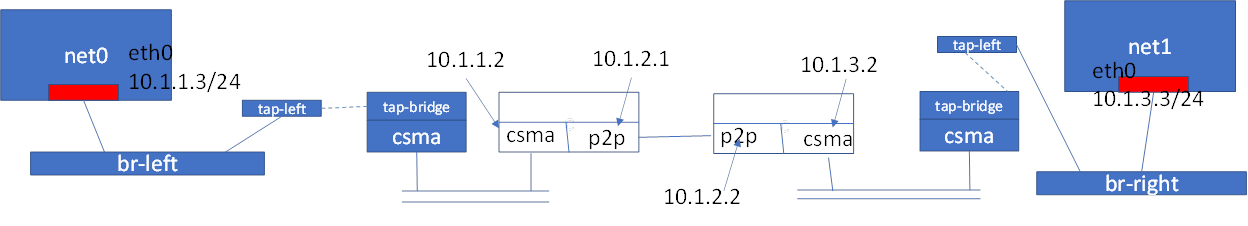
[Topology]
[Steps]
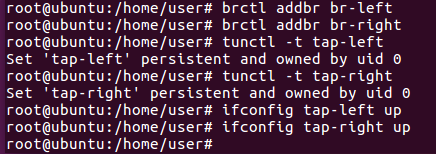
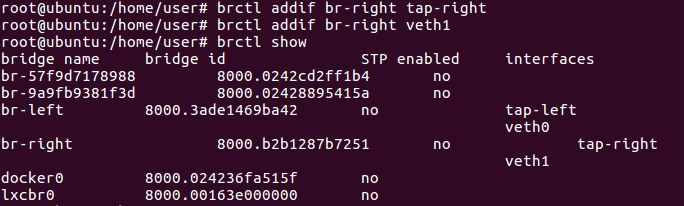
Create br-left and br-right bridges. Also create “tap-left” and “tap-right” taps.
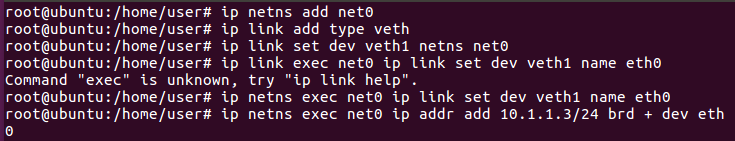
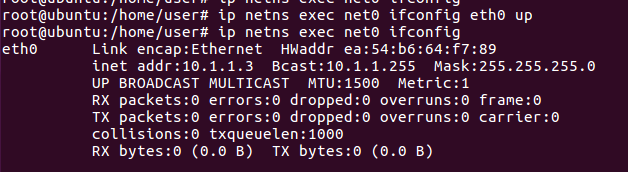
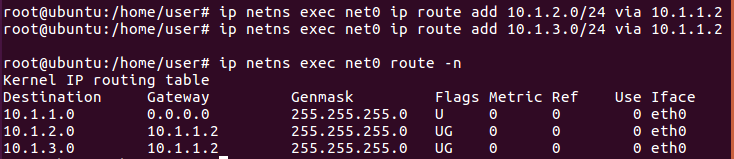
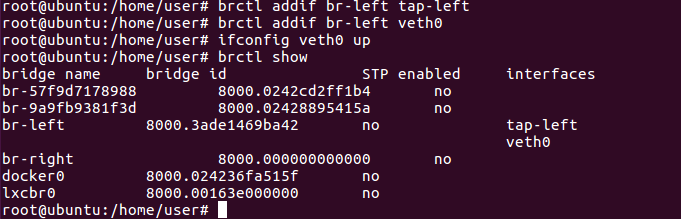
For the left-hand side namespace (net0)
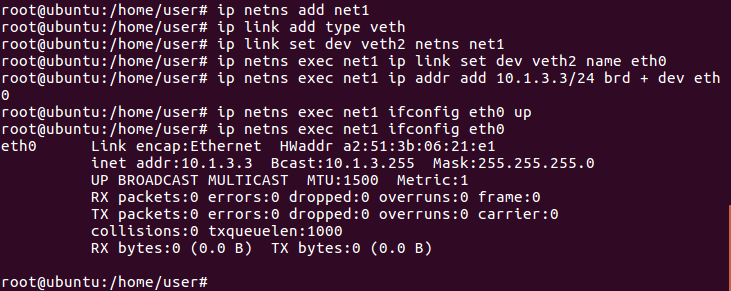
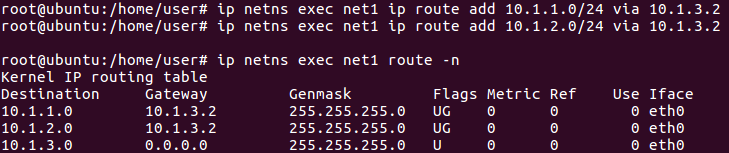
For the right-hand side namespace (net1)
![]()
![]()
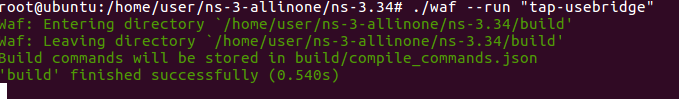
tap-usebridge.cc
|
/* -*- Mode:C++; c-file-style:"gnu"; indent-tabs-mode:nil; -*- */ /* * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as * published by the Free Software Foundation; * * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the * GNU General Public License for more details. * * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License * along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software * Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA */ // // This is an illustration of how one could use virtualization techniques to // allow running applications on virtual machines talking over simulated // networks. // // The actual steps required to configure the virtual machines can be rather // involved, so we don't go into that here. Please have a look at one of // our HOWTOs on the nsnam wiki for more details about how to get the // system confgured. For an example, have a look at "HOWTO Use Linux // Containers to set up virtual networks" which uses this code as an // example. // #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include "ns3/core-module.h" #include "ns3/network-module.h" #include "ns3/csma-module.h" #include "ns3/tap-bridge-module.h" #include "ns3/error-model.h" #include "ns3/point-to-point-module.h" #include "ns3/ipv4-global-routing-helper.h" #include "ns3/internet-module.h" using namespace ns3; NS_LOG_COMPONENT_DEFINE ("TapCsmaUseBridgeExample"); int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { CommandLine cmd (__FILE__); cmd.Parse (argc, argv); // // We are interacting with the outside, real, world. This means we have to // interact in real-time and therefore means we have to use the real-time // simulator and take the time to calculate checksums. // GlobalValue::Bind ("SimulatorImplementationType", StringValue ("ns3::RealtimeSimulatorImpl")); GlobalValue::Bind ("ChecksumEnabled", BooleanValue (true)); // // Create two ghost nodes. The first will represent the virtual machine host // on the left side of the network; and the second will represent the VM on // the right side. // NodeContainer csma1Nodes; csma1Nodes.Create (2); NodeContainer p2pNodes; p2pNodes.Add (csma1Nodes.Get (1)); p2pNodes.Create(1); NodeContainer csma2Nodes; csma2Nodes.Create(1); csma2Nodes.Add (p2pNodes.Get (1)); PointToPointHelper pointToPoint; pointToPoint.SetDeviceAttribute ("DataRate", StringValue ("5Mbps")); pointToPoint.SetChannelAttribute ("Delay", StringValue ("2ms")); NetDeviceContainer p2pDevices; p2pDevices = pointToPoint.Install (p2pNodes); CsmaHelper csma; csma.SetChannelAttribute ("DataRate", StringValue ("100Mbps")); csma.SetChannelAttribute ("Delay", TimeValue (NanoSeconds (6560))); NetDeviceContainer csma1Devices; NetDeviceContainer csma2Devices; csma1Devices = csma.Install (csma1Nodes); csma2Devices = csma.Install (csma2Nodes); Ptr<RateErrorModel> em = CreateObject<RateErrorModel> (); em->SetAttribute ("ErrorRate", DoubleValue (0.01)); em->SetAttribute ("ErrorUnit", StringValue ("ERROR_UNIT_PACKET")); p2pDevices.Get (1)->SetAttribute ("ReceiveErrorModel", PointerValue (em)); InternetStackHelper stack; stack.Install (csma1Nodes); stack.Install (csma2Nodes); Ipv4AddressHelper address; address.SetBase ("10.1.1.0", "255.255.255.0"); Ipv4InterfaceContainer csma1Interfaces; csma1Interfaces = address.Assign (csma1Devices); address.SetBase ("10.1.2.0", "255.255.255.0"); Ipv4InterfaceContainer p2pInterfaces; p2pInterfaces = address.Assign (p2pDevices); address.SetBase ("10.1.3.0", "255.255.255.0"); Ipv4InterfaceContainer csma2Interfaces; csma2Interfaces = address.Assign (csma2Devices);
Ipv4GlobalRoutingHelper::PopulateRoutingTables (); //TapBridgeHelper tapBridge; //tapBridge.SetAttribute ("Mode", StringValue ("ConfigureLocal")); //tapBridge.SetAttribute ("DeviceName", StringValue ("thetap")); //tapBridge.Install (csma1Nodes.Get (0), csma1Devices.Get (0)); // // Use the TapBridgeHelper to connect to the pre-configured tap devices for // the left side. We go with "UseBridge" mode since the CSMA devices support // promiscuous mode and can therefore make it appear that the bridge is // extended into ns-3. The install method essentially bridges the specified // tap to the specified CSMA device. //
TapBridgeHelper tapBridge; tapBridge.SetAttribute
("Mode", StringValue ("UseBridge")); tapBridge.SetAttribute
("DeviceName", StringValue ("tap-left")); tapBridge.Install (csma1Nodes.Get (0),
csma1Devices.Get (0)); // // Connect the right side tap to the right side CSMA device on the right-side // ghost node. //
tapBridge.SetAttribute
("DeviceName", StringValue ("tap-right")); tapBridge.Install (csma2Nodes.Get (0),
csma2Devices.Get (0)); // // Run the simulation for ten minutes to give the user time to play around // Simulator::Stop (Seconds (1000.)); Simulator::Run (); Simulator::Destroy (); } |
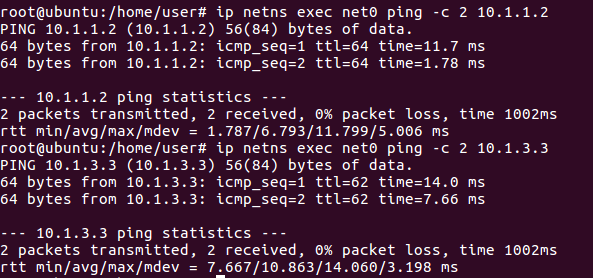
Open another terminal
In other terminal
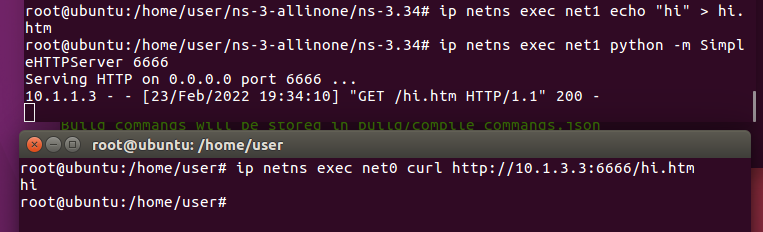
Last Modified: 2022/2/25 done
[Author]
Dr. Chih-Heng Ke
Department
of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Quemoy
University, Kinmen, Taiwan
Email:
smallko@gmail.com